What is a Private Key and Public Key Cryptography: How To Store & How It Works in Crypto
2024-05-02 03:55:15
What is a Private Key? What does it Have to Do with Crypto Wallets?
In cryptography, a private key is a secret code, similar to a password. private keys are used to sign cryptocurrency transactions and prove ownership of coins or a blockchain address.
A private key is fundamental to the functioning of cryptocurrency, knowing how to keep a private key safe is a vital part of protecting yourself from theft or loss of funds.
In short:
- • A private key is a secret cryptographic code that is used in cryptocurrency.
- • A private key is a randomly generated number with hundreds of digits, usually represented as alphanumeric strings.
- • Your crypto wallet consists of a public address and a private key. Anyone can send cryptocurrency to your public address, but funds can’t be moved from an address without your private key.
- • A private key is your final control and ownership of your cryptocurrency. It’s very important to never lose your private key or let anyone else know your private key.
The digital keys and addresses associated with cryptocurrency control virtual tokens. Public addresses can be used by anyone to deposit tokens. Even if a user has deposited tokens in their address, they will need the unique private key to withdraw them.
Private keys come in a few different forms which can be expressed as a string of characters. In base-ten notation, a private key would be hundreds of digits long and take years to crack by brute force. These days, most wallets further abstract the private key into “Seed words” which are a phrase of 12 or so words that allow you to easily recover your wallet.
A complex mathematical algorithm creates the public key from the private key. But it is practically impossible to reverse the process by generating a private key from a public key. Another algorithm creates a receiving address from the public key. Think of the address as a postbox, and the private key as your key to your postbox.
The postman or any passerby can post letters in to the postbox, but only the person with the key can open the postbox and get the letters and packages inside. It is important to keep the key safe so that no one else can take the mail. If the key is lost or stolen, then anyone could access the mailbox.
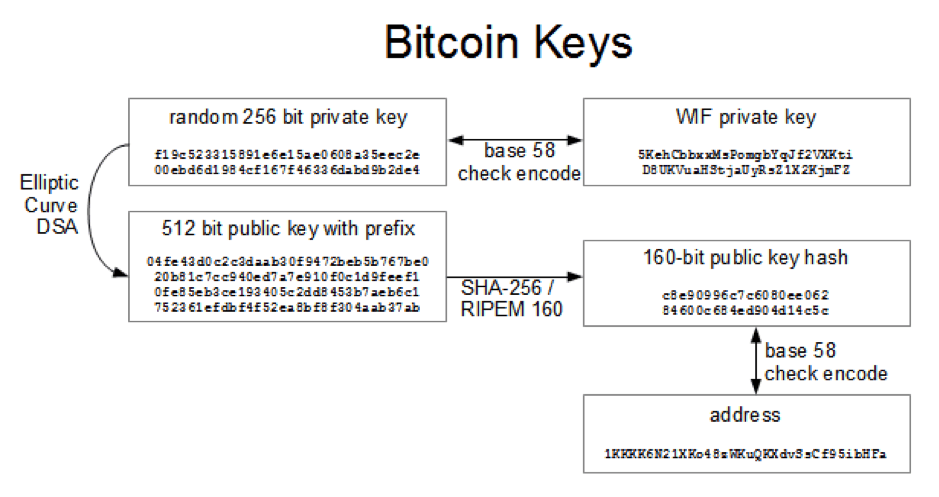
How do the two keys work? This diagram shows an example of a Bitcoin public key and private key. In daily usage, the 256 bit private key is base 58 encoded in to the WIF private key, and the public key is derived from the private key using the elliptic curve cryptographic algorithm and then further encrypted with SHA-256 in to a 160 bit public key hash and then encoded in to base 58 to become the public bitcoin address. It is computationally virtually impossible to derive the private key from the public address. In fact, even with the world’s most powerful supercomputer, it would take more than 3.3 Decillion years to crack one Bitcoin private key. That’s 3,300,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years!
Why Are Private Keys Important?
Private keys are used in most cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, to secure your funds. Your private key is the only thing that proves to the outside world that you own the cryptocurrency account or wallet. Anybody that knows your private key can move your coins. If someone else knows your private key, there is nothing stopping them from emptying your wallet.
The risks associated with private keys include loss and theft
If you are managing your own cryptocurrency wallet, the only way you can lose your coins is by losing your private key or someone discovers your private key and steals your coins.
These are some of the ways you can lose your private key:
- • Forget where you hid it after writing it down - If you’re not careful, you might easily misplace the piece of paper you wrote your private key down on.
- • It becomes damaged or destroyed - A written down private key can easily become damaged or destroyed by fire or flood. Pets or children may eat it by accident.
- • Throw it away by accident - whether written down or stored on a computer, many people have thrown away their private key by accident. One British man accidentally threw away his hard drive containing the private key to 7500 Bitcoins worth $280 Million dollars.
- • Delete it - If you saved your private key on your computer, it’s very easy to simply forget it and then restore or wipe your hard drive or save over the file during routine cleanups.
Apart from accidental loss, there are a wide variety of scams and thefts that unscrupulous criminals may use to relieve you of your private key.
- • Computer viruses - Hackers write malware and viruses that scan the victim’s computer for cryptocurrency private keys and then steal the coins.
- • Inside man - People often make the mistake of keeping their Private keys stored in “The cloud”. These have been stolen by systems administrators who have access to data stored on the cloud server.
- • Kidnap and extortion - A hardened criminal gang may simply kidnap you or a loved one and threaten to harm them or torture you until you give up your private key.
xkcd.com
The best way to keep your private key safe is to write it down and keep it somewhere where you won’t forget it, and it won’t be destroyed by water or heat and where no one apart from you will ever find it. After that, do not ever tell anyone you own cryptocurrency or they may try to steal it or extort you for your private key.
What is a Public Key and What is Public Key Cryptography?
Public-key cryptography (PKC) employs asymmetric encryption to verify the authenticity of data. PKC was initially used for encrypting and decrypting messages on standard computers. The technology that cryptocurrency transactions rely on for encryption and decryption is Public Key Cryptography. This technology would not be possible without trapdoor functions. Trapdoor functions are one-way mathematical functions that are easy to solve in one way, but nearly impossible to crack in the reverse. Even if it were possible, it would take a supercomputer thousands of years to reverse engineer these functions.
A cryptographic code that allows you to receive cryptocurrency transactions is called a public key. This code is paired with a corresponding private key, which is needed to unlock the transaction and prove ownership of the cryptocurrency. The public key is usually an address, which is a shortened form of the public key. You can share your public key without worry. For example, many content creators and charities post their crypto addresses' public keys online to accept donations. While anyone can donate, only the owner of the private key can unlock and access the donated funds.
In general, a bitcoin public key that starts with the number 1 would need a single private key to access the funds. There is another version though, called a multi-signature public key, that starts with the number 3. This type of key would require more than one private key to grant access to the funds.
How Public and Private Key Encryption Works?
How Does a Private Key Work? (In Asymmetric Cryptography)
Public and private keys form the basis of public key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography. In this system, every public key is linked to only one private key, and they work together to both encrypt and decrypt messages. By encoding a message with someone's public key, only their matching private key can be used to decode the message. Through public key cryptography, sensitive information and communications can be kept safe and secure.
What Does It Mean to “Digitally Sign” a Cryptocurrency Transaction?
A transaction request prompts the usage of a private key in order to sign the transaction and provide mathematical evidence that the cryptocurrency come from the owner. This is referred to as a signature, and it prevents the transaction from being modified by anyone else. Once a transaction is signed using the private key and validated, Cryptocurrencies are sent to and received by the other wallet; at this point, the transaction becomes irreversible.
How do you Sign a Message with a Private Key?
The process of signing a message can vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the wallet software you use. Some cryptocurrencies and wallets don't offer the option to sign messages.
Signing a message to your cryptocurrency address proves that you are the owner of the funds that the wallet holds. It also confirms that you control the private keys of that particular address, this provides further authentication than simply providing an address or transaction information through blockchain explorers where all information is public.
Consult your wallet software's documentation to determine the precise process for your specific wallet and cryptocurrency. If the wallet you use does not permit message signing (digital signature), but does enable the export of private keys or wallet seeds, it might be possible to import those private keys or seeds into another wallet program that does offer this capability.
What is a Bitcoin Address?
A Bitcoin address is a single-use token that acts as a virtual location to where cryptocurrency can be sent. Similarly to how fiat currencies can be sent to email addresses, people can send cryptocurrency to Bitcoin addresses. However, Bitcoin addresses are not meant to be permanent, but only for use in one transaction. Unlike a Bitcoin wallet, a Bitcoin address cannot hold bitcoins.
The alphanumeric string that is the address consists of 26-35 characters. This is the public half of an asymmetric key pair. The standard format for a Bitcoin address is P2PKH (pay to public key hash). Addresses are generated by Bitcoin wallets through cryptographic operations: The software generates a private key through an asymmetric signature algorithm and then derives the public key from the private one.
Bitcoin's beginnings saw users sending the currency to IP addresses. This was a convenient method, but it left users vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. To increase security, the Bitcoin address was created to make Bitcoin more secure.
• How to Use Your Public Key to Send Bitcoin
The public key can be utilized for sending cryptocurrency into a wallet. It is similar to how someone would provide their routing number and checking account number for direct deposit; however, it does not enable them to log in or withdraw money from the account. Think of the public key as the mailing address. Anybody can look it up and send cryptocurrency to that public key.
• How to Use Your Public Key to Receive Bitcoin
The public key is your bitcoin address. Similar to your home address, you would give it to anyone you want to be able to send mail to your house. You can provide your public key to anyone who might want to send bitcoins to your wallet. All public keys are searchable on a block explorer
Where Should You Store Your Private Keys?
It is ill-advised to store private keys in an online environment, via email, or in the cloud, as these are the most vulnerable to being hacked. Many people take screenshots of their private keys, which are often stored online through photo album syncing. This creates a security risk that should be avoided at all costs. Instead, keep them in various cold storage locations.
Cold storage means storage on a medium that isn’t connected to the internet. The simplest way is to write the private key down on a piece of paper and hide it somewhere safe. This is also known as a “Cold wallet”.
A hot wallet is a crypto wallet with its private key on a computer connected to the internet. This type of wallet is easier to transfer funds from quickly but because it is connected to the internet, is much more vulnerable to hacks and loss. A crypto exchange or financial institution may keep most of its funds in a cold wallet for security, and keep only part of its funds in a hot wallet to enable easy transfers.
Should You Trust a Custodial Wallet?
A third-party service that allows users to store cryptocurrency, similar to a bank, is known as a custodial wallet. Examples of custodial wallets include exchanges such as FAMEEX or Coinbase. This type of wallet enables users to bypass the complications of private key management by entrusting the security to the company offering the custodial wallet. However, there are some disadvantages. For example, custodial wallets can be compromised by hackers or phishing scams. They can also be seized or frozen by legal authorities or by the company itself. That’s not to say that self hosted wallets are impervious to phishing or hackers, they are not.
The best policy is to decide what type of wallet meets your personal level of technical ability and need for convenience. You can also use both self managed and custodial wallets at the same time. This is not an either, or, choice.
FAQ
• What is a private key bitcoin?
A private key is a secure code that allows the holder to safely conduct cryptocurrency transactions and prove ownership of their holdings. Bitcoin keys particularly feature a 256-bit string made up of a combination of letters and numbers for maximum security. With this advanced level of encryption, holders can make secure transactions with the utmost confidence.